ADSL Modules of H3C Series Routers
- 0关注
- 0收藏 584浏览
ADSL Modules of H3C Series Routers
I. Preface
With the rapid development and deep into the people’s heart of IT and network technologies, the requirement on network bandwidth is increasingly higher. Network construction and transformation wave are also stepping into peak period. At the same time, reducing network operation cost and introducing competition system will lead to a significant reduction of network construction investment. The building of new network and the alteration of existing network also have the same important characteristics, i.e. high performance and high bandwidth.
Previously, medium/low-end router can provide interfaces such as ISDN to meet the small and medium businesses requirements on Internet. Today, with the maturity and development of DSL technology, ADSL gradually becomes the main approach of SMB to access the Internet for its high bandwidth.
ADSL, also called as asymmetrical digital subscriber loop, is an asymmetrical version of xDSL. In general, ADSL can provide users with 32Kbps~8Mbps of downlink rate and 32K~1Mbps of uplink rate while not interfering the general communication services like voice or ISDN on the same line.
Enabling ADSL interface on medium/low end router can provide a new solution for various SMBs or some large branches and offices with requirements on high bandwidth. With digital code modulation technology, ADSL uses common line as transport media to directly connect to the operator’s DSLAM(Digital Subscriber's Loop Access Multiplexer)and then to ATM/IP backbone via DSLAM, meeting requirements such as high speed data communication and video on demand.
II. 1ADSL/2ADSL Module
1.Introduction
Huawei medium/low router R3600/R2600/R1760 supports one port ADSL interface module and two-port ADSL interface module, called as 1ADSL/2ADSL respectively. This module now supports enabling synchronous transmission of traditional POTS voice service and ADSL service on the same line, but not the synchronous transmission of ISDN service and ADSL service on the same line. It can be provided as enhanced features when there is such requirement in the market.
ADSL interface module is primarily used to provide uplink ADSL interface for a router in medium/lower router system. Its specified functions are as follows:
1. Support manually activate/deactivate ADSL line, support four loopback ways: analog, digital, utopia, sar and provide convenient troubleshooting methods;
2. Support three interface standards: G.DMT, G.Lite and T1.413, and can be configured as adaptive mode;
3. Support interleaving function of ADSL interface (except for G.Lite standard), enhancing the stability of ADSL connection.
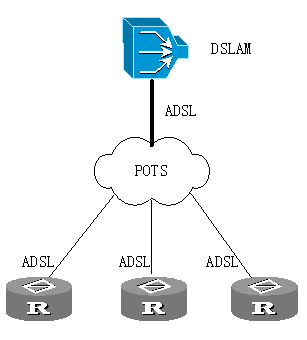
In medium/low router networking environment, ADSL interface module can be directly attached to DSLAM through one or two user lines, enabling the bandwidth interfaces of users. ADSL interface module can provide high performance applications with robust flexibility and confidentiality, especially the expenditure saving compared to traditional WAN access. Based on ATM technology, ADSL interface module provides VPN services. Combining with the analog/digital voice service provided, it allows providing different service levels for voice, mission-critical data, interactive multimedia and video and so on through VoIP. The following figure illustrates the ADSL interface module networking application.
![]()
Application of ADSL interface module of medium/low router in the network
2.Module Appearance
The appearance of one port ADSL module is similar to two-port ADSL module. The difference lies in the port number. The silk-screen on front panel can be used to differentiate these two modules. The appearance of 1ADSL/2ADSL module is as follows:
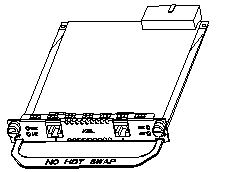
1ADSL module appearance
2ADSL module appearance
1ADSL module panel is shown as follows:

1ADSL module panel
The following table provides the implication of various indicators:
Implication of 1ADSL module indicators
|
LINK |
Extinguished represents that the corresponding port link is not connected; lighting represents that the corresponding port link is connected; flashing represents that the corresponding port is activating operator DSLAM device. |
|
ACT |
Extinguished represents the corresponding port has not received/sent data; flashing represents the corresponding port has received/sent data. |
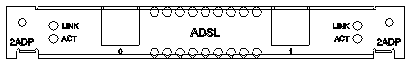
The following figure shows 2ADSL module panel:
2ADSL module panel
The following table provides the implication of various indicators:
Implication of 2ADSL module indicators 2ADSL
|
LINK |
Extinguished represents that the corresponding port link is not connected; lighting represents that the corresponding port link is connected; flashing represents that the corresponding port is activating operator DSLAM device. |
|
ACT |
Extinguished represents the corresponding port has not received/sent data; flashing represents the corresponding port has received/sent data. |
3.Module Interface Cable
1ADSL/2ADSL module interface cable is common line.
Note:
The standard configuration of 1ADSL/2ADSL module includes common line. User can independently purchase external spliter as required.
Connection of Module Interface Cable
To cabling ADSL-I module interface, installing a splitter is needed. Please cable according to the following steps:
Step 1: one side of line is attached to RJ11 socket of ADSL-1 module of a router, the other is attached to the internal ADSL-I interface of a splitter;
Step 2: use the second line to attach ISDN NT1 to the splitter;
Step 3: use the third line to attach the foreign ADSL-I interface of the splitter to POTS network.
4.ADSL Interface Parameters
The following table introduces ADSL module interface parameters:
1ADSL/2ADSL module interface attributes
|
Attributes |
1ADSL module |
2ADSL module |
|
Type of connector |
RJ11 | |
|
Interface number |
1 (1ADSL module) 2 (2ADSL module) | |
|
Interface rate |
Under ADSL Full Rate mode (i.e. ITU-T 992.1 G.DMT/ANSI T1.413): Downlink rate is 8Mbps, uplink rate is 1024Kbps. Under ADSL Lite mode (ITU-T 992.2 G.Lite): Downlink rate is 64Kbps~1.536Mbps, uplink rate is 64Kbps~512Kbps. | |
|
Interface standard |
ITU-T 992.1 G.DMT ITU-T 992.2 G.Lite ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 | |
|
Type of cable and maximum transmission distance |
ADSL module interface cable is line. Under Full Rate mode, the maximum distance is 1.8 Km (i.e. 6000 feet, the maximum transmission distance is associated with line quality); The normal distance is 5.5 Km (i.e. 18,000 feet). | |
|
Service |
ADSL access via common line | |
|
Supported protocol |
AAL5 IPOA PPPOA RFC 1483 (PPPOEOA and IPOEOA) F5 END TO END LOOPBACK OAM | |
|
Connection number |
One port 32 connections; two-port 64 connections | |
|
ATM QoS |
CBR, VBR-nrt, VBR-rt, UBR | |
|
QoS |
CAR, PQ, CQ, WFQ, CBWFQ, LFI | |
5.Networking Application
Quidway router configured with ADSL interface module is primarily used to access the Internet through ADSL line. There are following ways in terms of protocol configuration:
l PPPOEOA
l PPPOA
l IPOEOA
l IPOA
We will introduce these applications and configuration ways in the next sections:
a) PPPOEOA
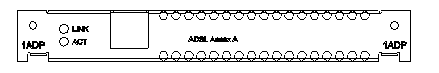
Figure 6 PPPOEOA method of router with ADSL module
This application method is shown as Figure 6:
LAN users access DSLAM (for example Huawei MA5100) through a shared Quidway 17/26/36 router and ADSL line. Then PP authentication is carried out by PPPoE Server (for example Huawei ISN8850 or Quidway NE series router). After authentication passed, user can access the Internet.
Also, user can configure trigger dial up and timeout handup features of PPPoE Client on the shared router in LAN, saving a maximum of online expense and maintenance cost.
In addition, the router directly runs PPPoE Client to obtain a public network address. This meets the network applications with requirements on public network addresses. In this application, the typical configuration of Quidway17/26/36 is as follows:
dialer-rule 1 ip permit
interface Dialer0
link-protocol ppp
ppp pap local-user aaa password simple aaa
ip address ppp-negotiate
dialer user aaa
dialer-group 1
dialer bundle 12
interface Atm 0/0
pvc 0/32
map bridge Virtual-Ethernet0 11-23-23
interface Virtual-Ethernet0
pppoe-client dial-bundle-number 12
If the device running PPPoE Server is also Huawei Quidway series router, you can refer the following configuration:
ip pool 0 10.1.1.3 10.1.1.10
local-user aaa password simple aaa
local-user aaa service-type ppp
interface Virtual-Template0
ppp authentication-mode pap
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
remote addr pool 0
interface Atm 0/0
pvc 0/32
map bridge Virtual-Ethernet0
interface Virtual-Ethernet0
pppoe-server bind Virtual-Template 0
b)PPPOA
The networking diagram of PPPOA is similar to Figure 6. The difference is that PPPOEOA is replaced by PPPOA. The reference configuration is as follows:
Server
ip pool 0 10.1.1.3 10.1.1.10
local-user abc password simple aaa
local-user abc service-type ppp
interface atm 0/0
pvc 0/32
map ppp virtual-template 0
interface virtual-template 0
ppp authentication-mode pap
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
remote addr pool 0
Client
Interface atm 0/0
Pvc 0/32
map ppp virtual-template 0
interface virtual-template 0
ppp pap local-user abc password simple aaa
ip address ppp-negotiate
The networking diagram of IPOA is also similar to Figure 6. Assuming that two routers are Router A and Router B respectively, the reference configuration is as follows:
Router A:
interface atm0/0
pvc 0/32
map ip default
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router B:
interface atm0/0
pvc 0/32
map ip default
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
d) IPOEOA
The networking diagram of IPOEOA is also similar to Figure 6. Assuming that two routers are Router A and Router B respectively, the reference configuration is as follows:
router A:
interface Virtual-Ethernet0
ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
interface Atm 0/0
pvc 0/32
map bridge Virtual-Ethernet0
Router B:
interface Virtual-Ethernet0
ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
interface Atm7/0
pvc 0/32
map bridge Virtual-Ethernet0 23-42-33
该案例暂时没有网友评论
编辑评论
✖
案例意见反馈


亲~登录后才可以操作哦!
确定你的邮箱还未认证,请认证邮箱或绑定手机后进行当前操作